Record
개념
- React : A JavaScript library for building user interfaces
목차
설명
npx create-react-app react-material-ui
yarn create react-app hooks-tutorial
선언형
React는 대화형 UI를 만드는 데 어려움을 줄입니다. 어플리케이션의 각 상태에 대한 간단한 뷰를 설계하면 React는 데이터가 변경될 때 적절한 구성요소만 효과적으로 업데이트하고 렌더링합니다.
선언형 뷰는 코드를 예측 가능하고 디버그하기 쉽게 만듭니다.
컴포넌트 기반
스스로 상태를 가지고 관리하는 캡슐화된 컴포넌트를 생성한 다음 복잡한 UI를 만들기 위해 구성합니다.
컴포넌트 로직은 템플릿 대신 JavaScript로 작성되므로, 앱을 통해 풍부한 데이터를 쉽게 전달하고 DOM에서 상태를 유지할 수 있습니다.
한번 배우고, 어디서나 작성한다
기술 스택의 나머지 부분에 대해 가정하지 않으므로, 기존 코드를 다시 작성하지 않고 React에서 새로운 기능을 개발할 수 있습니다.
React는 React Native를 이용하여 강력한 모바일앱을 만들거나 Node를 사용한 서버에서 렌더링할 수도 있습니다.
주요 개념
- JSX : JavaScript를 확장한 문법
- props : props 는 부모 컴포넌트가 자식 컴포넌트에게 주는 값. props 를 직접 수정 할 수 는 없습니다.
- state : state 는 컴포넌트 내부에서 선언하며 내부에서 값을 변경 할 수 있습니다.
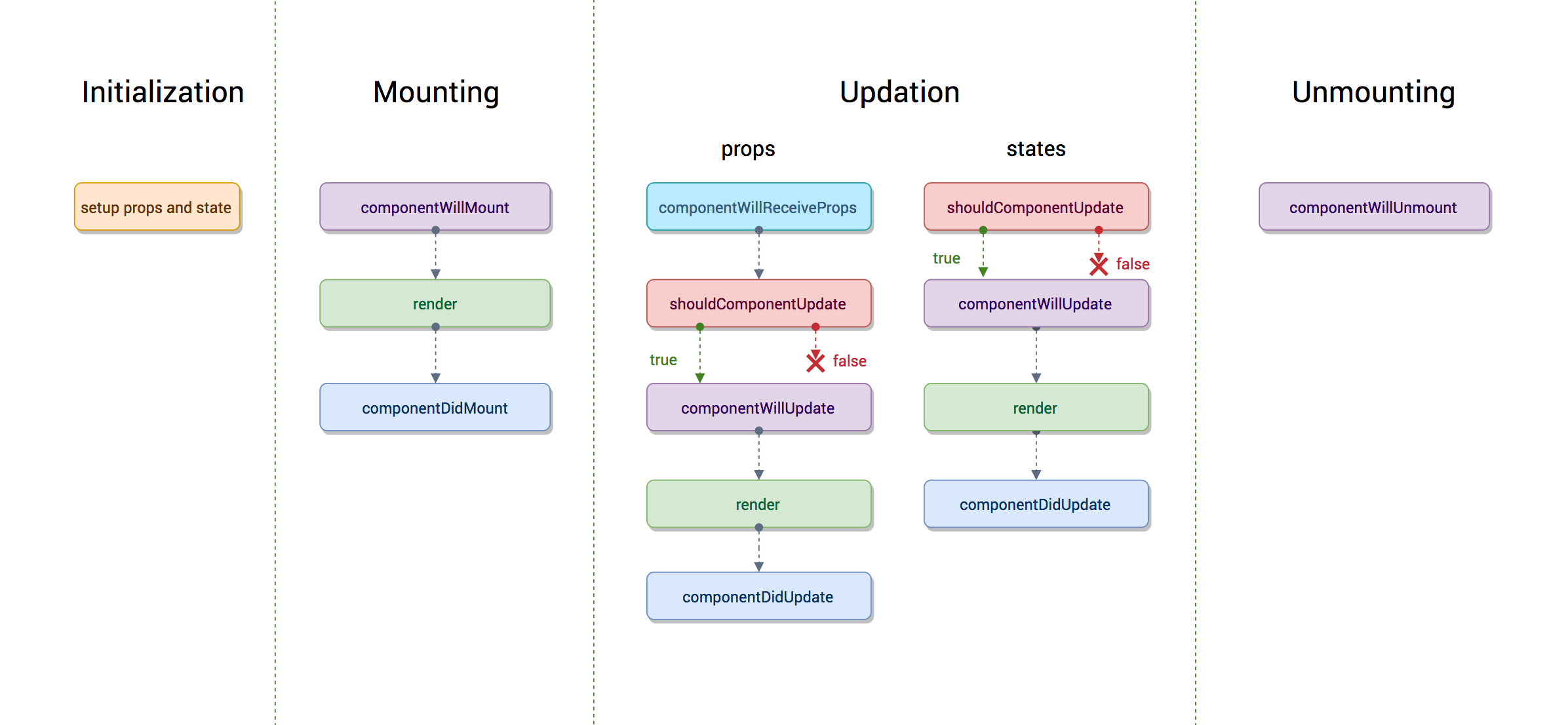
- flow
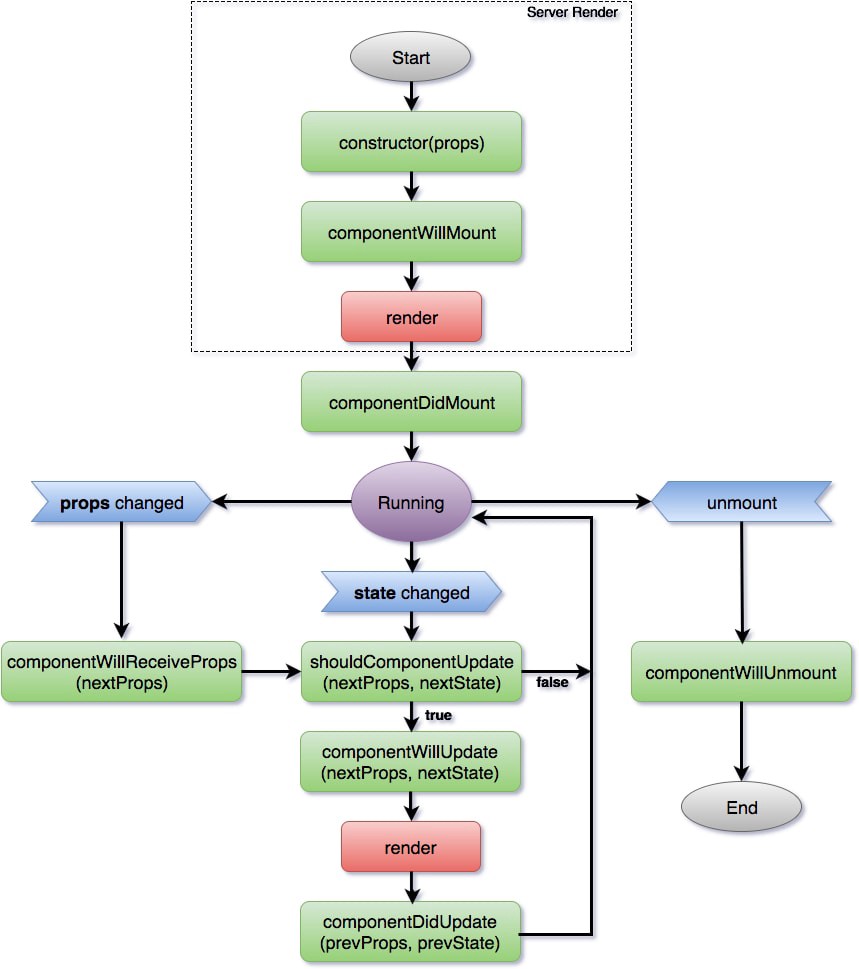
- Life Cycle
fetch
const res = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/');
const posts = await res.json();
axios
Axios는 HTTP통신을 하는데 매우 인기있는 Javascript라이브러리입니다. Axios는 브라우저와 Node.js 플랫폼에서 모두 사용할 수 있습니다.
또한 IE8이상을 포함한 모든 최신 브라우저를 지원합니다.
Axios는 Promise를 기반으로하여 async/await문법을 사용하여 XHR요청을 매우 쉽게 할 수 있습니다.
Fetch API보다 Axios가 더 좋은 장점은 아래와 같습니다.
구형브라우저를 지원합니다.(Fetch API의 경우는 폴리필이 필요합니다.) 요청을 중단시킬 수 있습니다. 응답 시간 초과를 설정하는 방법이 있습니다. CSRF 보호 기능이 내장되어있다. JSON 데이터 자동변환 Node.js에서의 사용
import axios from "axios";
axios.defaults.xsrfCookieName = "csrftoken";
axios.defaults.xsrfHeaderName = "X-CSRFToken";
axios.get(url), axios.post(url, data), axios.delete(url/id)
axios.post("/api/wisesaying/", { text: value }).then(res => this._renderText());
axios.get("/api/wisesaying/").then(res => this.setState({ textList: res.data })).catch(err => console.log(err));
axios.delete(`/api/wisesaying/${id}`).then(res => this._renderText());
fetch VS axios
let url = 'https://someurl.com';
let options = {
method: 'POST',
mode: 'cors',
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/json;charset=UTF-8'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
property_one: value_one,
property_two: value_two
})
};
let response = await fetch(url, options);
let responseOK = response && response.ok;
if (responseOK) {
let data = await response.json();
// do something with data
}
let url = 'https://someurl.com';
let options = {
method: 'POST',
url: url,
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/json;charset=UTF-8'
},
data: {
property_one: value_one,
property_two: value_two
}
};
let response = await axios(options);
let responseOK = response && response.status === 200 && response.statusText === 'OK';
if (responseOK) {
let data = await response.data;
// do something with data
}
Lists and Keys
- Lists
function NumberList(props) {
const numbers = props.numbers;
const listItems = numbers.map((number) => <li>{number}</li>);
return (
<ul>{listItems}</ul>
);
}
const numbers = [1,2,3,4,5];
ReactDOM.render(
<NumberList numbers={numbers} />,
document.getElementById('root')
);
- Keys : 중복되지 않는 값을 셋팅
Key로 값을 사용하는 방법
const number = [1,2,3,4,5];
const listItems = numbers.map((number) => <li key={number.toString()}>{number}</li>);
Key로 객체의 ID를 사용하는 경우
const todoItems = todos.map((todo) => <li key={todo.id}>{todo.text}</li>);
key로 index를 사용하는 경우
//Only do this if items have no stable IDs
const todoItems = todos.map((todo, index) => <li key={index}>{todo.text}</li>);
function ListItem(props){
return <li>{props.value}</li>;
}
function NumberList(props){
const numbers = pros.numbers;
const listItems = numbers.map((number) => <ListItem key={number.toString()} value={number} />);
return (
<ul>{listItems}</ul>
);
}
const numbers = {1,2,3,4,5};
ReactDOM.render(
<NumberList numbers={numbers}/>,
document.getElementById('root')
)
- Key 는 props로 전달되지 않는다!!!!, 전달이 필요하면 id에 Key값을 동일하게 셋팅
const content = posts.map((post) =>
<Post key={post.id} id={post.id} title={post.title} />
);
- Key 처리 JSX 문법으로 전환
function NumberList(props){
const numbers = pros.numbers;
const listItems = numbers.map((number) => <ListItem key={number.toString()} value={number} />);
return (
<ul>{listItems}</ul>
);
}
function NumberList(props){
const numbers = pros.numbers;
return (
<ul>{numbers.map((number) => <ListItem key={number.toString()} value={number} />)}</ul>
);
}
Form
- Controlled Components React 통제 받는 Input form element input 값의 변화가 모두 handleChange()에서 처리됨
handleChange(event) {
this.setState({value:event.target.value.toUpperCase()});
}
- textarea
<textarea value={this.state.value} onChange={this.handleChange}/>
- select
<select value={this.state.value} onChange={this.handleChange}>
<option value ="grapefruit">Grapefruit</option>
<option value ="lime">Lime</option>
<option value ="coconut">Coconut</option>
<option value ="mango">Mango</option>
</select>
<select multiple={true} value={['B','C']}>
<option value ="A">Grapefruit</option>
<option value ="B">Lime</option>
<option value ="C">Coconut</option>
<option value ="D">Mango</option>
</select>
- Uncontrolled Components : file input
<input type='file'/>
-
Multiple Inputs
-
Input Null Value
-
submit
class PhoneForm extends Component {
state = {
name: '',
phone: ''
}
handleChange = (e) => {
this.setState({
[e.target.name]: e.target.value
})
}
handleSubmit = (e) => {
// 페이지 리로딩 방지
e.preventDefault();
// 상태값을 onCreate 를 통하여 부모에게 전달
this.props.onCreate(this.state);
// 상태 초기화
this.setState({
name: '',
phone: ''
})
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<input
placeholder="이름"
value={this.state.name}
onChange={this.handleChange}
name="name"
/>
<input
placeholder="전화번호"
value={this.state.phone}
onChange={this.handleChange}
name="phone"
/>
<button type="submit">등록</button>
</form>
);
}
}
Lifting State Up
- 하위 state 를 상위로 올리는 기능, 상위에서 함수를 pros로 내린다. pros 의 함수에 값을 넣는다. 상위의 해당 함수는 해당 값을 state 에 넣는다.
class TemperatureInput extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this);
}
handleChange(e) {
this.props.onTemperatureChange(e.target.value);
}
render() {
const temperature = this.props.temperature;
const scale = this.props.scale;
return (
<fieldset>
<legend>Enter temperature in {scaleNames[scale]}:</legend>
<input value={temperature}
onChange={this.handleChange} />
</fieldset>
);
}
}
class Calculator extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleCelsiusChange = this.handleCelsiusChange.bind(this);
this.handleFahrenheitChange = this.handleFahrenheitChange.bind(this);
this.state = {temperature: '', scale: 'c'};
}
handleCelsiusChange(temperature) {
this.setState({scale: 'c', temperature});
}
handleFahrenheitChange(temperature) {
this.setState({scale: 'f', temperature});
}
render() {
const scale = this.state.scale;
const temperature = this.state.temperature;
const celsius = scale === 'f' ? tryConvert(temperature, toCelsius) : temperature;
const fahrenheit = scale === 'c' ? tryConvert(temperature, toFahrenheit) : temperature;
return (
<div>
<TemperatureInput
scale="c"
temperature={celsius}
onTemperatureChange={this.handleCelsiusChange} />
<TemperatureInput
scale="f"
temperature={fahrenheit}
onTemperatureChange={this.handleFahrenheitChange} />
<BoilingVerdict
celsius={parseFloat(celsius)} />
</div>
);
}
}
Composition
- Containment
- 여러개의 컴포넌트를 합쳐서 새로운 컴포넌트를 만드는 것
- props children : 컴포넌트 안에 있는 모든 JSX 태그를 children으로 전달됨
function SplitPane(props){
return (
<div>{props.children}</div>
);
}
function App() {
return (
<SplitPane>
<h1 className="ccls">Welcome</h1>
<p className="pcls">Thank</p>
</SplitPane>
);
}
props.children
<h1 className="ccls">Welcome</h1>
<p className="pcls">Thank</p>
function SplitPane(props){
return (
<div>
<div>{props.left}</div>
<div>{props.right}</div>
</div>
);
}
function App() {
return (
<SplitPane
left ={<Contacts/>}
right = {<Chat/>}
/>
);
}
props.left
<Contacts/>
props.right
<Chat/>
Specialization
- 전문화, 특수화
- Specialization <- Composition
Containment와 Specialization을 같이 사용
Inheritance
- 상속
- 다른 컴포넌트로부터 상속을 받아서 새로운 컴포넌트를 만드는 것
Hooks
최상위(at the Top Level)에서만 Hook을 호출해야 합니다 오직 React 함수 내에서 Hook을 호출해야 합니다 React 함수 컴포넌트에서 Hook을 호출하세요. Custom Hook에서 Hook을 호출하세요.
- useState : 함수형 컴포넌트에서도 상태 관리를 할 수 있는 Hook
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const Info = () => {
const [name, setName] = useState('');
const [nickname, setNickname] = useState('');
const onChangeName = e => {
setName(e.target.value);
};
const onChangeNickname = e => {
setNickname(e.target.value);
};
return (
<div>
<div>
<input value={name} onChange={onChangeName} />
<input value={nickname} onChange={onChangeNickname} />
</div>
<div>
<div>
<b>이름:</b> {name}
</div>
<div>
<b>닉네임: </b>
{nickname}
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default Info;
- useEffect : 리액트 컴포넌트가 렌더링 될 때마다 특정 작업을 수행하도록 설정 할 수 있는 Hook componentDidMount componentDidUpdate componentWillUnmount
useEffect(() => {
console.log('마운트 될 때만 실행됩니다.');
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
console.log(name);
}, [name]);
useEffect(() => {
console.log('effect');
console.log(name);
return () => {
console.log('컴포넌트가 언마운트되기 전이나, 업데이트 되기 직전에 어떠한 작업을 수행하고 싶다');
console.log('cleanup');
console.log(name);
};
});
- useContext : 함수형 컴포넌트에서 Context 를 보다 더 쉽게 사용 할 수 있습니다
import React, { createContext, useContext } from 'react';
const ThemeContext = createContext('black');
const ContextSample = () => {
const theme = useContext(ThemeContext);
const style = {
width: '24px',
height: '24px',
background: theme
};
return <div style={style} />;
};
export default ContextSample;
- useReducer : 리듀서는 현재 상태와, 업데이트를 위해 필요한 정보를 담은 액션(action) 값을 전달 받아 새로운 상태를 반환하는 함수입니다
- useMemo : useMemo Hook 을 사용하면 이러한 작업을 최적화 할 수 있습니다. 렌더링 하는 과정에서 특정 값이 바뀌었을 때만 연산을 실행하고 만약에 원하는 값이 바뀐 것이 아니라면 이전에 연산했던 결과를 다시 사용하는 방식입니다
import React, { useState, useMemo } from 'react';
const getAverage = numbers => {
console.log('평균값 ? 계산중..');
if (numbers.length === 0) return 0;
const sum = numbers.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
return sum / numbers.length;
};
const getAverage2 = numbers => {
console.log('평균값 O 계산중..');
if (numbers.length === 0) return 0;
const sum = numbers.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
return sum / numbers.length;
};
const UseMemoSample = () => {
const [list, setList] = useState([]);
const [number, setNumber] = useState('');
const onChange = e => {
setNumber(e.target.value);
};
const onInsert = e => {
const nextList = list.concat(parseInt(number));
setList(nextList);
setNumber('');
};
const avg = useMemo(() => getAverage(list), [list]);
return (
<div>
<input value={number} onChange={onChange} />
<button onClick={onInsert}>등록</button>
<ul>
{list.map((value, index) => (
<li key={index}>{value}</li>
))}
</ul>
<div>
<p><b>평균 값(useMemo):</b> {avg}</p>
<p><b>평균 값(렌더링 될때 마다 실행):</b> {getAverage2(list)}</p>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default UseMemoSample;
-
useCallback : useMemo Hook 처럼 렌더링 성능을 최적화해야 하는 상황, 컴포넌트가 렌더링 될 때 단 한번만 함수가 생성됨. 컴포넌트를 여러번 사용할 경우 최적화 필요
-
useRef : useRef Hook 은 함수형 컴포넌트에서 ref 를 쉽게 사용 할 수 있게 해줍니다. Average 컴포넌트에서 등록 버튼을 눌렀을 때 포커스가 인풋 쪽으로 넘어
import React, { useState, useMemo, useRef } from 'react';
const getAverage = numbers => {
console.log('평균값 계산중..');
if (numbers.length === 0) return 0;
const sum = numbers.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
return sum / numbers.length;
};
const Average = () => {
const [list, setList] = useState([]);
const [number, setNumber] = useState('');
const inputEl = useRef(null);
const onChange = useCallback(e => {
setNumber(e.target.value);
}, []); // 컴포넌트가 처음 렌더링 될 때만 함수 생성
const onInsert = useCallback(
e => {
const nextList = list.concat(parseInt(number));
setList(nextList);
setNumber('');
inputEl.current.focus();
},
[number, list]
); // number 혹은 list 가 바뀌었을 때만 함수 생성
const avg = useMemo(() => getAverage(list), [list]);
return (
<div>
<input value={number} onChange={onChange} ref={inputEl} />
<button onClick={onInsert}>등록</button>
<ul>
{list.map((value, index) => (
<li key={index}>{value}</li>
))}
</ul>
<div>
<b>평균 값:</b> {avg}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default Average;
ref 안의 값은 바뀌어도 컴포넌트가 렌더링 되지 않는다는 점 입니다. 렌더링과 관련 되지 않은 값을 관리 할 때만 이러한 방식
import React, { useRef } from 'react';
const RefSample = () => {
const id = useRef(1);
const setId = (n) => {
id.current = n;
}
const printId = () => {
console.log(id.current);
}
return (
<div>
refsample
</div>
);
};
export default RefSample;
-
useInputs : useReducer 로 해결했던 작성했던 로직을 useInputs 라는 Hook 으로 따로 분리
-
usePromise : 함수형 컴포넌트에서 Promise 를 더 쉽게 사용 할 수 있는 Hook
- useImperativeHandle
- useLayoutEffect
- useDebugValue : React 개발자도구에서 사용자 Hook 레이블을 표시하는 데에 사용할 수 있습니다.
function useFriendStatus(friendID) {
const [isOnline, setIsOnline] = useState(null);
// ...
// Show a label in DevTools next to this Hook
// e.g. "FriendStatus: Online"
useDebugValue(isOnline ? 'Online' : 'Offline');
return isOnline;
}
- Customs Hooks
// 경로 : src/lib/useInput.js
import { useState } from 'react';
const useInput = (initialValue) => {
const [value, setValue] = useState(initialValue);
const onChange = e => {
// Destructing Assignment
const { target: { value } } = e;
setValue(value);
}
return [ value, setValue, onChange ];
}
export default useInput;
// 경로 : src/App.js
import React, { useState } from "react";
import InputBox from "./components/InputBox";
import PhoneList from "./components/PhoneList";
import "./App.css";
import { dummyData, nextId, setNextId } from "./lib/dummyData.js";
import useInput from './lib/useInput';
const App = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState(dummyData);
const [name, setName, onChangeName] = useInput("");
const [phone, setPhone, onChangePhone] = useInput("");
const handleSubmit = () => {
};
const handleRemove = id => {
};
return (
<div className="container">
<InputBox
name={name}
phone={phone}
onChangeName={onChangeName}
onChangePhone={onChangePhone}
onSubmit={handleSubmit}
/>
<PhoneList list={data} deleteItem={handleRemove} />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
// 경로 : src/components/InputBox/InputBox.js
import React from "react";
import styles from "./InputBox.module.css";
const InputBox = ({ name, phone, onChangeName, onChangePhone, onSubmit }) => {
return (
<div className={styles.input_boxes}>
<div className={styles.input_box}>
<div className={styles.input_box_name}>이름</div>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="이름"
name="name"
className={styles.input_box_input}
onChange={onChangeName}
value={name}
/>
</div>
<div className="input_box">
<div className={styles.input_box_name}>전화번호</div>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="전화번호"
name="phone"
className={styles.input_box_input}
onChange={onChangePhone}
value={phone}
/>
</div>
<button className={styles.input_box_button} onClick={onSubmit}>
저장
</button>
</div>
);
};
export default InputBox;
Redux 리덕스
- flow
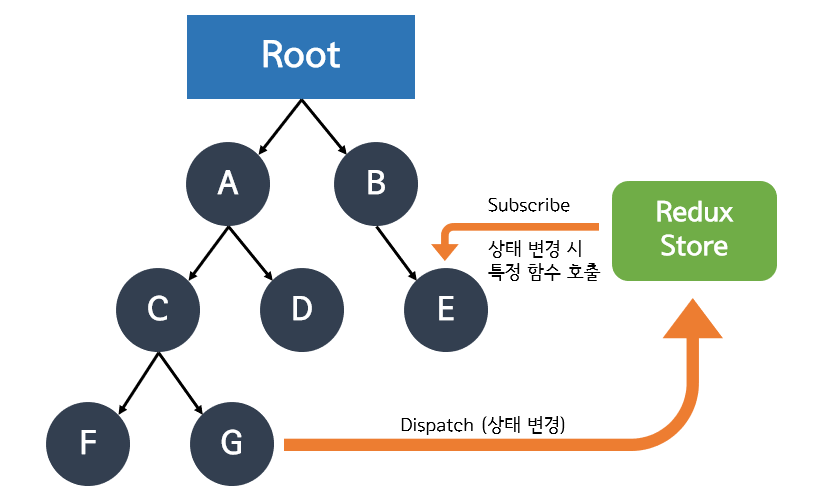
- State (상태)
- Store (스토어) : Redux 앱에서는 단 하나의 스토어만 허락됨
- Action (액션) : 상태를 변화시키려는 것을 표현하는 객체, type 필드는 꼭 가지고 있어야 함
{
type : "couter/INCREASE", //필수
value: 1
}
- Action Creators (액션 생성자) : 액션만 만들며, 스토어에 실제 요청을 보내지 않음
const increase = value => ({
type: "couter/INCREASE",
value: 1
});
- Dispatch (디스패치 함수) : 액션을 인자값으로 받고, 인자값으로 받은 액션을 스토어에 보내 상태관리를 요청함. 스토어에서 요청을 받으면 해당 액션을 실행
store.dispatch(increase(10))
- Reducer (리듀서) : 실제 상태 변화가 발생하는 함수이고, Dispatch를 통한 요청을 받으면 실행되는 함수, 해당 액션 객체의 type 값에 따라 특정 함수를 실행시키고, 새로운 상태를 만들어 반환함
Redux 3대 원칙
-
Single source of truth
- 모든 상태는 하나의 스토어 안에 하나의 객체 트리 구조로 저장
-
State is read-only
- 상태 변화는 액션 객체를 전달하는 방법뿐, 모든 상태 변화는 중앙에서 관리되고, 엄격한 순서로 실행
-
Changes are made with pure functions
- 리듀서 함수 내부에서 네트워크, 데이터베이스 접근, Math, Date 같은 순수하지않은 API를 호출하는 코드가 있으면 안됨
함수
- import { combineReducers } from ‘redux’; 리듀서를 하나로 합치
- import { createStore } from ‘redux’; createStore 와 루트 리듀서 불러오기
- import { Provider } from ‘react-redux’; 리액트 프로젝트에 스토어를 연동
- import { connect } from ‘react-redux’; connect 함수를 사용하여 컴포넌트에 스토어 연동하기
- import { bindActionCreators } from ‘redux’; // **** (1) 불러오기
- import { createAction } from ‘redux-actions’;
- import { handleActions } from ‘redux-actions’;
개발도구
리덕스 개발을 더욱 편하게 하기 위해서 Redux Devtools 라는 크롬 확장프로그램 // **** 리덕스 개발자도구 적용 const devTools = window.REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION && window.REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION();
Mobx 1
-
yarn add mobx mobx-react
-
yarn eject
-
yarn add @babel/plugin-proposal-class-properties @babel/plugin-proposal-decorators
"babel": {
"presets": [
"react-app"
],
"plugins": [
["@babel/plugin-proposal-decorators", { "legacy": true}],
["@babel/plugin-proposal-class-properties", { "loose": true}]
]
}
개발도구
- yarn add mobx-react-devtools import DevTools from ‘mobx-react-devtools’;
Mobx 2
import { observable } from 'mobx'
import { Observer, useObserver, observer } from 'mobx-react-lite'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import React from 'react'
const person = observable({
name: 'John'
})
const P1a = observer(function P1a({ person }) {
return <h1>{person.name}</h1>
})
const P1b = observer(({ person }) => <h1>{person.name}</h1>)
const P2 = ({ person }) => <Observer>{() => <h1>{person.name}</h1>}</Observer>
const P3 = ({ person }) => useObserver(() => <h1>{person.name}</h1>)
const rootElement = document.getElementById('root')
ReactDOM.render(
<div>
<P1a person={person} />
<P1b person={person} />
<P2 person={person} />
<P3 person={person} />
<i>All names will change after 2 seconds</i>
</div>,
rootElement
)
setTimeout(() => {
person.name = 'Elizabeth'
}, 2000)
prop-types
- Proptypes를 이용한 타입 체크 만일 isRequired로 정의되어 있는데 부모 컴포넌트에서 해당 props을 전달하지 않으면 브라우저 콘솔에 다음과 같은 warning이 출력된다.
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
class Greeting extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<h1>Hello, {this.props.name}</h1>
);
}
}
Greeting.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string
};
index.js:1 Warning: Failed prop type: The prop `handleIncrease` is marked as required in `HandleView`, but its value is `undefined`.
in HandleView (at Count.js:20)
in Count (at src/index.js:6)
- 기본 Prop 값 defaultProps 속성을 사용하면 props 의 기본 값을 할당할 수 있습니다.
class Greeting extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<h1>Hello, {this.props.name}</h1>
);
}
}
// Specifies the default values for props:
Greeting.defaultProps = {
name: 'Stranger'
};
class Greeting extends React.Component {
static defaultProps = {
name: 'stranger'
}
render() {
return (
<div>Hello, {this.props.name}</div>
)
}
}
- 단일 자식 요구하기 PropTypes.element 를 사용하면 하나의 컴포넌트만 자식으로써 전달되게 할 수 있습니다.
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
// This must be exactly one element or it will warn.
const children = this.props.children;
return (
<div>
{children}
</div>
);
}
}
MyComponent.propTypes = {
children: PropTypes.element.isRequired
};
MyComponent.propTypes = {
// You can declare that a prop is a specific JS primitive. By default, these
// are all optional.
optionalArray: PropTypes.array,
optionalBool: PropTypes.bool,
optionalFunc: PropTypes.func,
optionalNumber: PropTypes.number,
optionalObject: PropTypes.object,
optionalString: PropTypes.string,
optionalSymbol: PropTypes.symbol,
// Anything that can be rendered: numbers, strings, elements or an array
// (or fragment) containing these types.
optionalNode: PropTypes.node,
// A React element.
optionalElement: PropTypes.element,
// You can also declare that a prop is an instance of a class. This uses
// JS's instanceof operator.
optionalMessage: PropTypes.instanceOf(Message),
// You can ensure that your prop is limited to specific values by treating
// it as an enum.
optionalEnum: PropTypes.oneOf(['News', 'Photos']),
// An object that could be one of many types
optionalUnion: PropTypes.oneOfType([
PropTypes.string,
PropTypes.number,
PropTypes.instanceOf(Message)
]),
// An array of a certain type
optionalArrayOf: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.number),
// An object with property values of a certain type
optionalObjectOf: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.number),
// An object taking on a particular shape
optionalObjectWithShape: PropTypes.shape({
color: PropTypes.string,
fontSize: PropTypes.number
}),
// You can chain any of the above with `isRequired` to make sure a warning
// is shown if the prop isn't provided.
requiredFunc: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
// A value of any data type
requiredAny: PropTypes.any.isRequired,
// You can also specify a custom validator. It should return an Error
// object if the validation fails. Don't `console.warn` or throw, as this
// won't work inside `oneOfType`.
customProp: function(props, propName, componentName) {
if (!/matchme/.test(props[propName])) {
return new Error(
'Invalid prop `' + propName + '` supplied to' +
' `' + componentName + '`. Validation failed.'
);
}
},
// You can also supply a custom validator to `arrayOf` and `objectOf`.
// It should return an Error object if the validation fails. The validator
// will be called for each key in the array or object. The first two
// arguments of the validator are the array or object itself, and the
// current item's key.
customArrayProp: PropTypes.arrayOf(function(propValue, key, componentName, location, propFullName) {
if (!/matchme/.test(propValue[key])) {
return new Error(
'Invalid prop `' + propFullName + '` supplied to' +
' `' + componentName + '`. Validation failed.'
);
}
})
};
성능분석
-
구글에 React DevTools 를 검색해서 크롬 웹스토어에 들어간뒤, 크롬 확장 프로그램을 설치해주세요. 설치를 하고 나면 다음과 같이 React 탭이 개발자 도구에 뜹니다. 톱니바퀴 아이콘을 누르고, ‘Highlight Updates’ 를 체크해주세요.
-
Components 탭을 이용해 props와 state를 확인하고 변경가능하다.
- component 우측에 있는 3가지 버튼을 활용하면 좋다
- Inspect : 어떤 HTML 태그를 렌더링 됬는지 Element 태그로 이동하여 알려준다.
- Debugging : 해당 컴포넌트의 정보를 console 태그에 알려준다.
- View Soure : 해당 컴포넌의 jsx 파일 알려준다.
-
Profiler 탭을 이용해서 최적화가 됬는지 안됬는지 확인할 수 있다.
- useMemo, useCallback을 쓰고 나서 얼마나 효과가 있는지 확인 할 수 있다.
- 녹화버튼을 눌러 해당 컴포넌트의 렌더링/이벤트을 녹화하여 시간을 알려준다.
Eject 사용안하기
- 반드시 Eject하지 않아도 기존 CRA프로젝트에 약간의 customizing을 할 수 있는 방법이 있다.(물론, Eject하는것보다 자유롭진 않다.) customize-cra와 react-app-rewired는 나의 CRA프로젝트를 eject하지 않고 customizing할 수 있게 도와주는 라이브러리이다. 현재 CRA2 버전을 사용하고 있다면 customize-cra와 react-app-rewired를 같이 사용하고, CRA1버전을 사용하고 있다면 react-app-rewired만을 사용하면 된다.
yarn create react-app cra_not_eject\
cd cra_not_eject
yarn add customize-cra --dev
yarn add react-app-rewired --dev
/* package.json */
"scripts": {
"start": "react-app-rewired start",
"build": "react-app-rewired build",
"test": "react-app-rewired test --env=jsdom"
}
- Customize-CRA 로 Decorator 설정 추가해보기
yarn add --dev @babel/plugin-proposal-decorators
config-overrides.js
const {
addDecoratorsLegacy,
disableEsLint,
override
} = require("customize-cra");
module.exports = {
webpack: override(
disableEsLint(),
addDecoratorsLegacy()
)
};

